Dental erosion, isn’t that the same as tooth decay?
No, dental erosion is the loss of tooth substance itself due to the direct action of acids in the mouth. It is different from tooth decay which is softening of the tooth by acid produced by bacteria feeding on sugars in the diet.
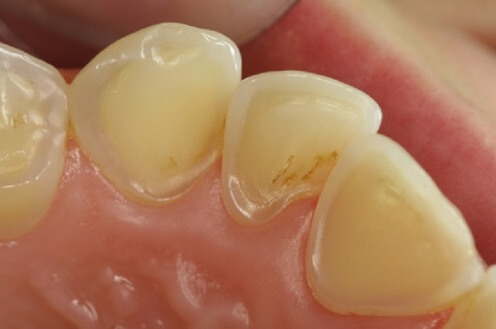
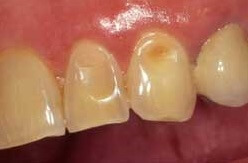
What causes dental erosion?
Every time you eat or drink something acidic the enamel (the hard outer coating of the tooth) is softened. Saliva helps to re-harden the enamel but frequent acid attacks means the mouth cannot repair itself and small amounts of enamel are lost. Over time the tooth surface starts to be lost. When the enamel is worn away, the softer dentine below is exposed which can lead to sensitivity & pain.
Am I at risk from dental erosion?
• Anyone who drinks large amounts of fruit juices or carbonated (fizzy) drinks is at risk
• If you have a medical condition such as hiatus hernia or other oesophageal disorders which cause acid from the stomach to regurgitate into the mouth (gastro-oesophageal reflux), you are also at increased risk.
• Patients who suffer with with anorexia nervosa or bulimia have a higher risk of dental erosion too.
If fruit causes dental erosion, should I still eat it?
Yes – fruit is an important part of a healthy, balanced diet and a good source of many vitamins. We can advise you how to reduce the risk of dental erosion from fruit.
How do I know if I have dental erosion?
To begin with there are often no symptoms of dental erosion and it is diagnosed following a dental examination. As the enamel is gradually lost the front teeth can appear thinner and more translucent, whilst the back teeth can develop hollows in the biting surface.
The teeth gradually become weaker and start to chip and may eventually appear shorter. As the dentine starts to be exposed you
Can I help prevent dental erosion?
• Reduce the number of times each day that acidic foods and drinks are consumed. Limit them to mealtimes wherever possible
• If you cannot avoid acidic drinks, have them as cold as possible with lots of ice and drink them through a straw
• Rinse your mouth with water or a fluoride mouthwash after acidic foods and drinks
• Chew sugar free gum for 20 minutes after eating and drinking to encourage re-hardening of the tooth surface by saliva
• Wait at least 30 minutes after acidic foods and drinks before brushing your teeth so you don’t brush the softened enamel away
Should I use a special toothpaste?
We advise you use a fluoride toothpaste twice a day. We may also recommend a tooth paste with a higher level of fluoride and /or fluoride rinses and gels.
If you have any questions about dental erosion, please ask a member of the dental team.





